BNCT treatments for cancer patients have started as part of a clinical trial
Keywords:HUS has introduced the first in-hospital boron neutron capture therapy accelerator in Western countries. Boron neutron capture therapy, BNCT for short, is a radiation therapy method that can destroy cancer cells while sparing the surrounding tissue.
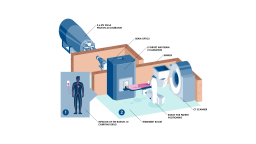
Before the neutron irradiation, the patient is administered a boron delivery agent intravenously. The delivery agent transports the boron into the cancer cell. At the top in in the image is the particle accelerator which produces a proton shower, in the middle is the target, which turns protons into neutrons, and on the bottom is the treatment room where the neutrons are targeted toward the patient’s tumor. The treatment room is also equipped with a CT scanner to ensure the patient's correct position before the treatment. Vesa Sammalisto | HUS
The first cancer patients received treatment with BNCT at Comprehensive Cancer Center in May as part of a study.
The launch of the treatments at HUS Comprehensive Cancer Center was made possible through a multi-year collaborative effort with the North American company Neutron Therapeutics. The Comprehensive Cancer Center was chosen as a partner because of the high quality of scientific BNCT research carried out at the center since 1992.
“The first BNCT center in Western countries presents a unique opportunity to develop this promising treatment method in close collaboration with Finnish and international research groups and offer cancer patients the chance to participate in various clinical trials,” says Johanna Mattson, Director of HUS Comprehensive Cancer Center.

The particle accelerator in HUS BNCT-center Mikko Hinkkanen HUS
Neutron capture therapy is targeted radiotherapy that spares the surrounding tissue
Boron neutron capture therapy, BNCT for short, is a type of targeted radiotherapy based on the decay reaction that occurs in boron atom nuclei delivered to the cancerous tumor when it is irradiated with neutrons.
Before the neutron irradiation, the patient is administered a boron delivery agent intravenously. The delivery agent accumulates in the cancer cells and delivers the boron inside the cells.
When the tumor area is irradiated with neutrons, it results in a very high local dose of radiation therapy in the cancer cells that contain boron.
“Short-range radiation effectively destroys the cancer cells while sparing the surrounding tissue. This requires fewer treatments than traditional radiation therapy, only one or two,” says Chief Medical Physicist Mikko Tenhunen from HUS Comprehensive Cancer Center.
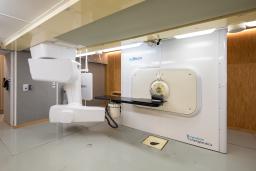
Treatment room in HUS BNCT-center Mikko Hinkkanen HUS
The efficacy and safety of BNCT is being investigated in a clinical trial
A study was started at the Comprehensive Cancer Center to treat ten patients who have recurrent cancer in the head and neck area. The study assesses the safety and efficacy of BNCT.
“The goal is to extend the research program to other cancers in the future. Developing BNCT as a treatment also involves combining it with different cancer drugs and researching potential new boron delivery agents,” says Anu Anttonen, chief physician responsible for radiation therapy at HUS Comprehensive Cancer Center.